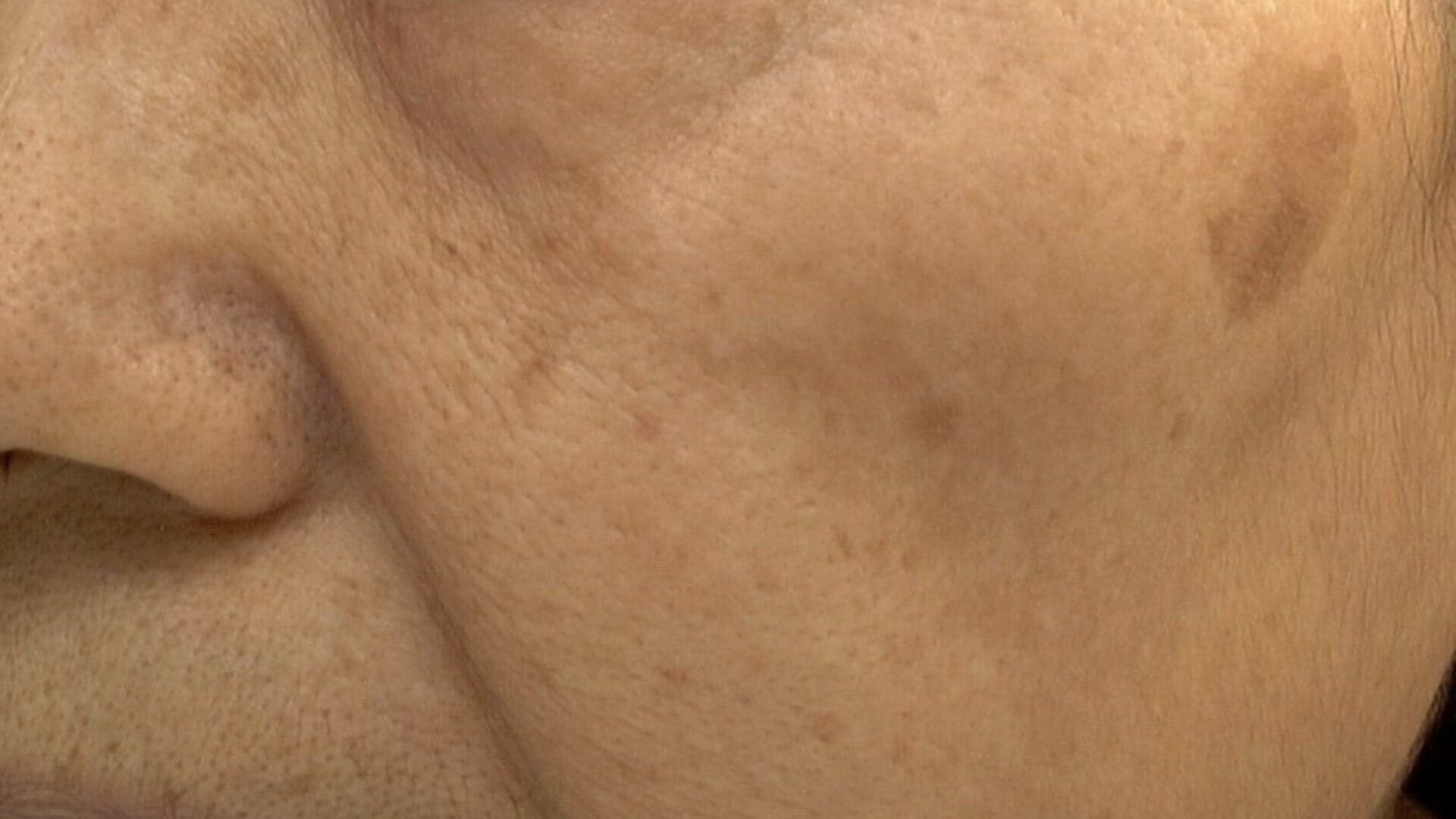
When we age, it is inevitable that your skin is going to change, wrinkles, fine lines and pigmentation. Whilst we like to put the process down to ageing, the main issue is photoaging which is caused by exposure to sunlight and ultraviolet light, this is responsible for 90% of visible changes to the skin. Light is around us all year, making sun damage a year-round concern for healthy skin, so whilst chronological skin aging can’t be helped, photoaging accelerates the process.
Luckily, aspects of photoaging are preventable if you know how, one of the most visible signs is pigmentation. To help understand how to prevent pigmentation from appearing on your skin, aesthetic specialist at Candela Medical, Chanele Rosa has shared exactly what pigmentation is and the different ways you can treat it.
1) What is pigmentation?
Pigmentation is the colour of your skin. Hyperpigmentation can be referred to as the darkening of the skin and skin pigmentation disorders can cause changes to the skin colour. A pigmented lesion is caused by an abnormal production of melanin (pigment) which makes it visible to the skin surface such as sun- spots / age spots.
2) Can life factors influence pigmentation?
Yes, sun exposure and tanning beds are the biggest factor which rapidly darken existing pigment and stimulate the melanocytes to produce more pigment. However hormonal changes can also influence pigmentation and appears as symmetrical, blotchy brown facial pigment, this type of pigmentation is known as melasma or the pregnancy mask. Other factors include inflammatory conditions such as acne and various forms of dermatitis like eczema.
3) Where can it be on the body?
Pigmentation can affect patches of your skin or your entire body. Pigmentation can appear anywhere on the body. Mostly areas that are exposed to the sun such as the face, chest, arms and legs. After our skin is exposed to sun, we might get a few freckles which then fade in the winter, this is the body’s effort to protect skin cells from UV damage. Freckles might become permanent and the UV damage might be not visible until we get older when they rise the surface as ‘age’ spots on either your hands, face or cleavage. These can be darker and permanent if preventive measures aren’t applied.
4) What different ways are available to treat pigmentation?
Lasers and IPL are the most advanced treatments that can safely and effectively remove pigmentation. The Nordlys by Candela has been successful at removing pigmentation by using narrowband IPL. The system has 3 wavelengths 400nm for resistant pigmentation, 530nm and 555nm for deeper pigmentation.
The treatment works by the light being attracted to the melanin within the lesion. Light is converted into heat and heats the pigment to 70C which effectively shatters the pigment (Phototoxic reaction). The shattered pigment then desquamates with the skin cell turnover, where it will naturally shed, and any remaining pigment will appear lighter. 1 to 3 treatments are recommended at 4-week intervals. Lightening Products that contain a pigment suppressant and sun protection is also recommended to treat pigmentation.
5) How can you prevent pigmentation?
Avoid direct sun exposure and tanning beds as this can lead to long term effects of pigmentation. An SPF 50 + should be worn daily and reapplied throughout the day, even in the winter where the sun isn’t visible. Avoid picking and scratching at the skin to prevent hyperpigmentation.
6) How can you stop pigmentation reoccurring?
You can use cosmeceutical products that are specific to treating pigmentation, this will help supress the pigment. An SPF 50 + should be worn daily and reapplied throughout the day if you are not exposed to the sun.